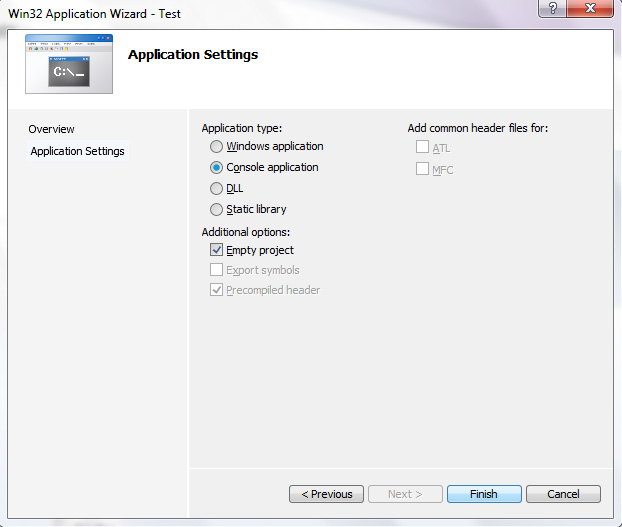
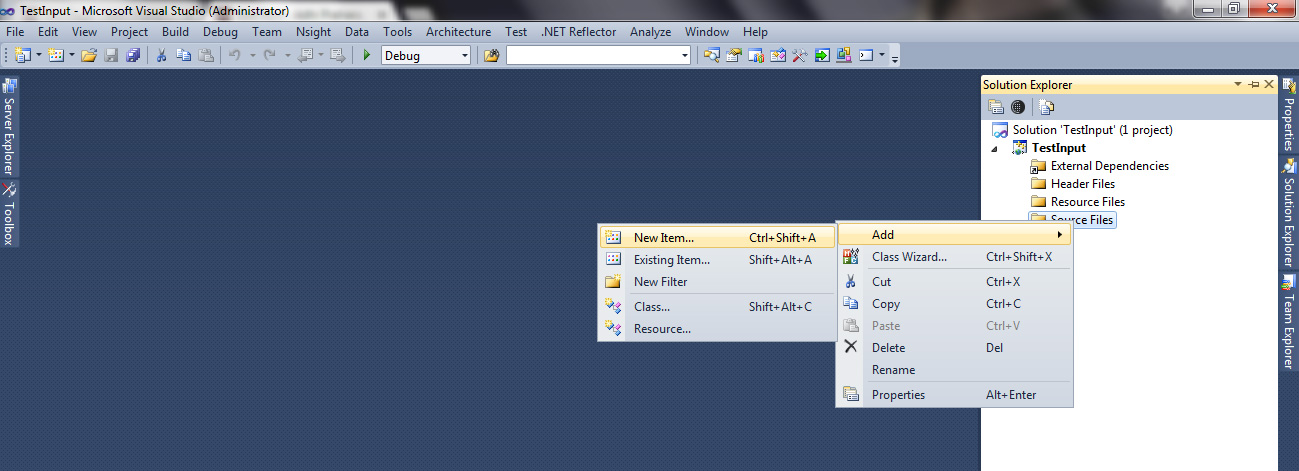
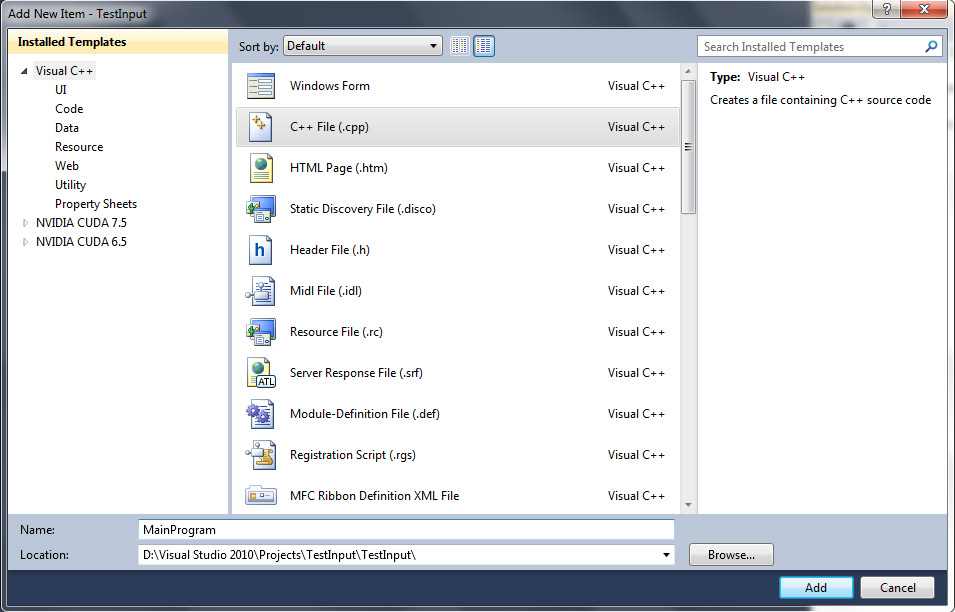
This tutorial will show you how to use class in C++. This is the class standard format :
class name_of_class
{
private:
// write private variables or function here
public:
// write public variables or function here
};
The difference between class and struct is the visibility. Struct declaration is always public while class can be set into private or public. To understand more about class in C++, we will make a simple class to create Point3D data type just like what we do in constructor section. Suppose we want to create a constructor to handle 3D data type which contain coordinate X, Y and Z.
Add this to your header in .cpp file
#include <math.h>
Write this code in your .cpp.
// create a class to handle coordinates 3D
class Point3D
{
public:
// declare public variable coordinate X, Y and Z
float X;
float Y;
float Z;
float Magnitude;
// create an empty constructor
Point3D() { };
// create a constructor to fill Point3D data type
Point3D(float x, float y, float z)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
Z = z;
calcMagnitude();
};
// check if constructor is empty
bool isEmpty()
{
if (X != NULL && Y != NULL && Z != NULL)
return false;
return true;
};
// create a desctructor to destroy Point3D data type
~Point3D() { };
private:
// calculate magnitude from this point3D
void calcMagnitude()
{
Magnitude = isEmpty() ? 0 : sqrt(pow(X, 2) + pow(Y, 2) + pow(Z, 2));
}
};
// main function
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int key;
// create a Point3D data type named point
// insert X = 2.2, Y = 3.1 and Z = 4.5
Point3D point(2.2, 3.1, 4.5);
// read the value
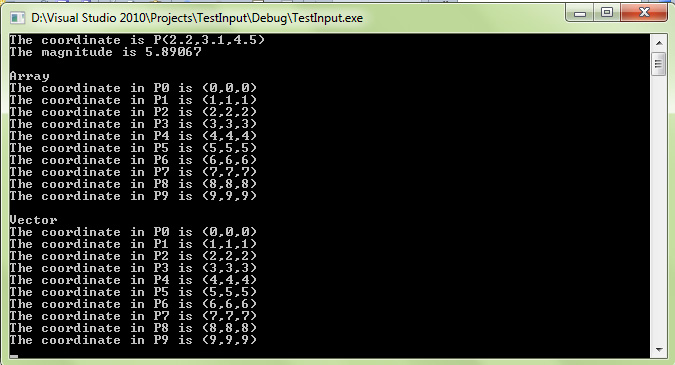
cout << “The coordinate is P(“ << point.X << “,” << point.Y << “,” << point.Z << “)\n”;
cout << “The magnitude is “ << point.Magnitude << “\n”;
cout << “\nArray\n”;
// create an array of Point3D data type
Point3D* arrayPoint = new Point3D[10];
// fill the array of point using for loop
for (int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
arrayPoint[i] = Point3D(i, i, i);
cout << “The coordinate in P” << i << ” is (“ << arrayPoint[i].X << “,” << arrayPoint[i].Y << “,” << arrayPoint[i].Z << “)\n”;
}
// don’t forget to destroy the array if it is not used
delete[] arrayPoint;
cout << “\nVector\n”;
// create vector of Point3D data type
vector<Point3D> listPoint;
// fill the vector of point using for loop
for (int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
listPoint.push_back(Point3D(i, i, i));
cout << “The coordinate in P” << i << ” is (“ << listPoint[i].X << “,” << listPoint[i].Y << “,” << listPoint[i].Z << “)\n”;
}
// don’t forget to empty the vector if it is not used
listPoint.clear();
cin >> key;
return 0;
}
This is the result :